Credit Information Report (CIR)
About Credit Score
1. What is a Credit Score?
A Credit Score is a three digit numeric summary of your credit history. The value ranges between 300-900.It is derived by using details found in the Accounts and Enquiries section on your Credit Information Report (CIR). It indicates the ‘probability of default’ of a borrower based on their credit history.
2. What role does a credit score play in the loan application process?
Your Credit Score is one of the first checks that a lender does when they are evaluating your Loan application. It’s important to know that nearly 90% of the loans are granted for individuals with score greater than 700.
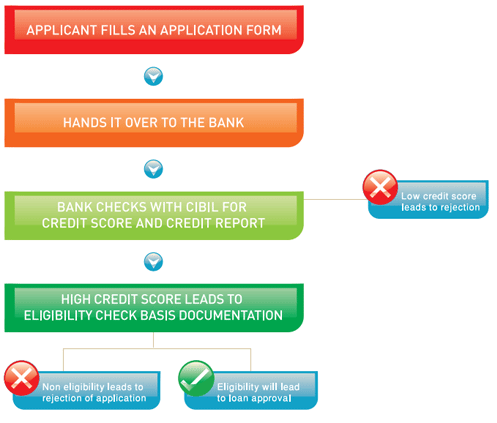
3. How does one determine their loan eligibility?
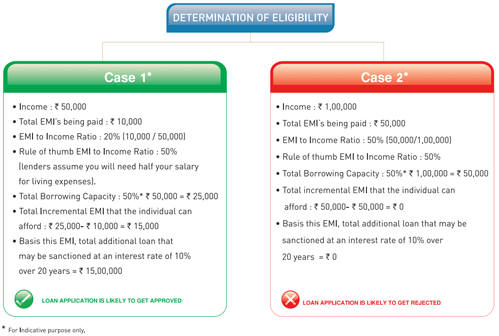
Loan eligibility is determined using information such as Income, Current EMIs, and Credit Score.Once a Credit Score meets the lenders internal credit policy criteria, they then analyze the documents to understand some key points as below.
In addition to the above fields the lenders also look at the:
- Payment history - If there is a consistent irregularity noticed in your re-payment pattern then this is viewed negatively
- Number of new “enquiries” - If there are too many lenders enquiring your Credit details (as you may have applied for loans/Credit card with multiple lenders) then this may make you appear “Credit Hungry” which is viewed negatively
How to read your Credit Score and CIR
4. How do you read a CIR?
A Credit Information Report (CIR)has detailed information on the credit you have availed, such as home loans, credit cards, personal loans, automobile loans, overdraft facilities. Credit Score report is divided into 6 sections :
-
CIBIL TransUnion Score
The CIBIL TransUnion Score reflects your Credit health or your Credit worthiness

-
Personal Information
It contains your Personal details (Name, PAN Card, DOB) as reported by Banks. Make sure this information is accurate.

-
Contact Information
Various contact details provided by various lenders is recorded here. Up to 4 latest addresses are recorded here.

-
Employment Information
Monthly or annual income details are captured here as reported by thelenders. Only the latest reported detail will reflect.

-
Account Information
Contains the details of your credit facilities includingnames of lenders, type of credit facilities (home, auto, personal, overdraft, etc.), account numbers, ownership details, date opened, date of last payment, loan amount, current balance and a month on month record(of up to 3 years) of your payments.

The below section represents your payment behavior. Any irregularity in payment is recorded here.
lease check the glossary section to understand the terms in detail.

-
Enquiry Information
This section details out which lenders are requesting for/enquiring your credit details. The purpose for which the enquiry is made and the approximate amount for it is highlighted in this section.

Loan Rejections and Disputes
5. Why are applicants asked to contact CIBIL if their loan has been rejected?
One of the parameters considered by lenders when evaluating a loan application is the Credit Score. The loan would have been rejected because the Credit score does not meet the lenders internal Credit policy criteria. By contacting CIBIL you can purchase your Credit Score and CIR and understand your credit history in detail. The report will indicate the areas that are adversely affecting the Credit score or will help you identify any discrepancies/errors that maybe reflecting against your name.
6. What are the types of disputes/errors that can be raised with CIBIL?
You can contact us if you notice any error in your report. The types of dispute that can be raised are :
- Personal information: Information such as Name, Date of Birth, Pan, Address etc.
- Account Information:Information such as Account/ Loan Type, status, date of last payment, current balance, amount overdue etc can be disputed. If you purchased your CIR within 45 days of making the last payment, it may not be updated yet. However, if the ‘Date Reported’ is older than 2 months, write to CIBIL to update the information
- Ownership: Make sure all personal details and accounts belong to you. If an account does not match, raise a dispute
- Duplicate Account: If the same account is reflecting more than once, you can get this rectified

7. How do you improve your credit score
You need to maintain a good credit history to be viewed favorably by lenders, and this can be done by following 7 simple rules :
- Rule 1: Always pay your bills on time. Late payments are viewed negatively by Loan providers and may affect the chances of your loan getting approved
- Rule 2: Keep your balances low. While the balances on your loans will only reduce over time as payments are made, you must be diligent about making timely payments on your credit cards. Also, you should control your utilization. For example, if you have used Rs. 90,000 out of a credit limit of Rs. 1,00,000, this may be viewed negatively by a Loan provider. It’s always prudent to not use too much credit
- Rule 3: Maintain a healthy mix of credit. Your credit history should contain a mix of a home loan, auto loan and a couple of credit cards. A high number of just credit cards may affect the chances of a loan approval. Why is it so, you may wonder. Although a credit card offers easy access to finance, it’s also by far the most expensive form of credit. More the number of credit cards with high utilization, larger are the payments resulting from its high rate of interest
- Rule 4: Apply for new credit in moderation. If you have made many applications for loans, or have recently been sanctioned new credit facilities, a Loan provider is likely to view your application with caution. This ‘Credit Hungry’ behaviour indicates your debt burden is likely to, or has increased and you are less capable of honouring any additional debt
- Rule 5: Think twice before closing credit card accounts. While, using credit cards may negatively impact your credit history, unused credit cards actually imply that you are financially secure. This makes Loan providers view your application more favourably
- Rule 6: Monitor your co-signed and joint accounts monthly. In co-signed or jointly held accounts, you are held equally liable for missed payments. This is extremely important because your joint holder’s negligence could affect your ability to access credit when you need it
- Rule 7: Review your credit history frequently throughout the year. Unpleasant surprises in the form of rejected loan applications can be avoided by ensuring that your CREDIT REPORT accurately reflects your current financial status. So reviewing your credit history 3-4 times each year is imperative
Case Study
How a ‘good’ credit history helps in getting lower rates for loans
Mr. Roy wanted a car worth 10.29 lacs, he had 4 lacs andneeded an auto loan of 6.29 lacs. He applied for a loan from Bank A, who offered him a quote of 11.70% for a 5 year period; the EMI would be 13,897.Mr. Roy also approached Bank B, who checked his Credit Information Report and Credit Score and offered a lower rate of 11.30% for the same term, bringing down the EMI by 126. Mr. Roy called Bank A to decline their offer since Bank B had given him a better quote. On learning this, Bank A matched the offer by giving him a rate of 10.34%; the EMI would be 13,470, resulting in a total saving of 25,604 over the 5 years.Mr. Roy’s good credit history, credit score, and financial discipline earned him almost a 3% discount on an auto loan.
Glossary

-
Accounts - Only credit facilities get reported on your CIR, such as home, auto and personal loans, overdraft facilities, credit cards, and loan against shares. Assets including savings account, fixed deposits, mutual funds and stock investments do not get reported
-
Closed loan accounts - A loan account that has been closed by the lender if you have paid off your loan. It could also be closed if you have not paid off the full loan amount but the status of the account is ‘Written Off and Settled’
-
‘NA’ or ‘NH’ - A Score of “NA” or “NH” is not a bad thing at all. These mean one of the below:
- You do not have a credit history or you do not have enough of a credit history to be scored, i.e. you are new to the credit system
- You do not have any credit activity in the last couple of years
- You have all add-on credit cards and have no credit exposure











